

Vertical pumps, as one of the important equipment in the field of liquid transportation and processing, have many types and wide applications. How much do you know about vertical pumps? Are you aware of the different types of vertical pumps and their critical role in different industries? In this article, we will take an in-depth look at various vertical pump types, revealing their working principles, characteristics, and applications in various fields such as water supply, drainage, chemicals, sewage treatment, and more. Let’s explore the world of vertical pumps together.
Table of contents:
A vertical pump is a vertically arranged pump, which is characterized by the fact that the pump motor and pump body are arranged in the vertical direction. This type of pump usually sucks in and discharges liquid by rotating an impeller and has a special structure.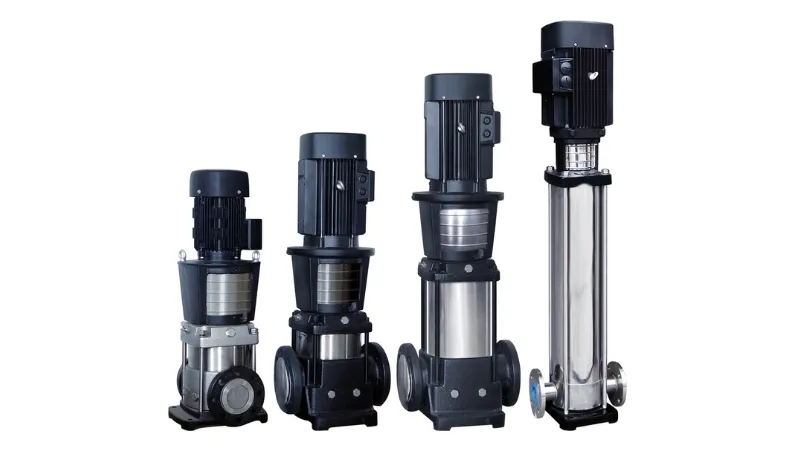 They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and functions, but all have a unique vertical configuration that moves liquid vertically upward through a pipe. They can be used at a variety of operating temperatures from low to high, at different pressures, and with a wide range of liquids, from ordinary water services to corrosive, flammable, and even difficult-to-handle liquids and chemicals.
They come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and functions, but all have a unique vertical configuration that moves liquid vertically upward through a pipe. They can be used at a variety of operating temperatures from low to high, at different pressures, and with a wide range of liquids, from ordinary water services to corrosive, flammable, and even difficult-to-handle liquids and chemicals.
When work begins, the impeller of the vertical pump is located at the bottom of the pump body. The suction port at the bottom of the pump body is exposed to the liquid, and the liquid is introduced into the pump. The pump's motor creates a low-pressure area by rotating the impeller, causing liquid to be drawn into the pump body.
Once the liquid is sucked into the pump body, it is lifted by the rotational power of the impeller. The rotational speed and design of the impeller affects the flow rate and pressure increase of the liquid.
When the liquid is lifted high enough, it will enter the discharge pipe. The top of the pump body usually has a discharge port through which the liquid is discharged out of the pump body and delivered to the desired destination. This process creates areas of high pressure that allow the liquid to overcome pipe resistance and be sent out. Vertical pumps keep the fluid flowing by continuously rotating the impeller, constantly sucking in, lifting and expelling fluid.
Construction features:
Vertical arrangement: The motor and the pump body of the vertical centrifugal pump are usually arranged vertically on the same axis, which makes the overall height of the pump lower and suitable for installation and operation in a limited space.
Motor Location: The motor is located on the top of the pump body and is usually the driving part of the pump. This design helps to reduce liquid residue at the bottom of the pump and reduces the air cavity of the pump, thereby improving water absorption efficiency.
Suction and discharge port locations: The suction port of a vertical centrifugal pump is located at the bottom of the pump, while the discharge port is usually located at the top of the pump. The liquid is drawn into the pump body through the suction port, and then pumped out through the discharge port.
Shaft seal design: In order to prevent liquid leakage, vertical centrifugal pumps usually use different types of shaft seals to ensure the reliability and safety of the pump.
Application areas:
Vertical centrifugal pumps are widely used in a variety of industrial and municipal applications, including but not limited to the following applications:
Water supply and drainage system: used in urban water supply and drainage systems, and industrial water treatment.
Cooling system: used for cooling equipment and machinery, such as cooling towers and cooling cycles.
Wastewater treatment: Used to transport wastewater from treatment facilities to downstream treatment areas.
Chemical process: In chemical production, it is used to transport various chemical liquids.
Structural features:
Submersible design: The main feature of the vertical submersible pump is that its motor and pump body are completely submerged in the liquid. This design allows the pump to operate in liquids without the need to build special supports or mounting equipment above ground.
Motor and pump body location: The motor is usually located at the top of the pump body, while the suction port at the bottom of the pump body is used to suck in liquid. The motor generates negative pressure by rotating the impeller, sucking the liquid into the pump body, and then discharging the liquid through the drainage pipe.
Special sealing and insulation: Since the motor and other internal components must operate in liquid, vertical submersible pumps are often equipped with special sealing and insulation systems to ensure the safety of the motor and prevent liquid penetration.
Application areas:
Vertical submersible pumps are typically used in the following applications:
Drainage and wastewater treatment: Used in drainage systems, wastewater treatment plants and industrial wastewater treatment to pump liquids away from low-lying areas.
Water supply system: Used in water supply systems to provide clean drinking water or industrial water.
Groundwater extraction: Used to pump groundwater for purposes such as irrigation, construction projects, or underground mining.
Marine applications: Used in marine engineering such as marine research, submarine pipeline installation and marine resource development.
Structural features:
Vertical arrangement: The main feature of a vertical turbine pump is that its motor and pump body are arranged in a vertical direction. The motor is located at the top of the pump body, while the turbine or impeller is located at the bottom of the pump body. This vertical layout allows the pump to operate efficiently in confined spaces.
vertical layout allows the pump to operate efficiently in confined spaces.
Motor location: The motor is usually located in the upper part of the pump body and is connected to the turbine or impeller through a shaft. The rotational power of the motor is transmitted to the turbine, causing it to rotate and generate negative pressure, thereby sucking liquid into the pump body.
Suction and discharge port positions: The liquid is sucked into the pump body through the suction port, and then pushed to the top of the pump body, and discharged to the required location through the discharge port.
Multi-stage design: Vertical turbine pumps usually have a multi-stage design, with turbines and impellers arranged in certain levels to increase the pump's pressure boosting capacity. Each level increases the pressure of the liquid.
Application areas:
Vertical turbine pumps are typically used in the following applications:
Water supply system: Used in urban water supply systems to pump water from a source or storage tank into the water supply network.
Industrial Applications: Used for liquid transfer in industrial processes such as the chemical, pharmaceutical and power industries.
Cooling system: Used in cooling towers, cooling cycles and air conditioning systems to maintain the normal operation of equipment and machinery.
Marine applications: Used in marine engineering such as deep sea drainage and oil field extraction.
Structural features:
Vertical arrangement: The motor and pump body of a vertical sewage pump are usually arranged vertically on the same axis, making the overall height of the pump relatively low and suitable for installation and operation in limited spaces.
Motor location: The motor is usually located at the top of the pump body, while the suction port at the bottom of the pump body is used to suck in sewage. The motor generates negative pressure by rotating the impeller or turbine, which sucks sewage into the pump body.
Suction and discharge port locations: The suction port of a vertical sewage pump is usually located at the bottom of the pump, while the discharge port is located at the top of the pump body. This design helps to reduce the air cavity of the pump, improve water absorption efficiency, and effectively discharge the treated sewage.
Special sealing and insulation: Since the vertical sewage pump is used to handle liquids containing solid particles and contaminants, it is usually equipped with special sealing and insulation systems to ensure the reliability of the pump and prevent liquid leakage.
Application areas:
Vertical sewage pumps are widely used in the following application areas:
Sewage treatment plant: Used to remove collected sewage from ponds or sewer pipes and send it to treatment equipment for treatment.
Urban drainage system: Used in urban drainage systems to discharge rainwater and sewage from urban areas to downstream treatment areas.
Industrial Applications: Used to treat industrial wastewater in industrial processes such as pharmaceutical, chemical and manufacturing industries.
Construction Engineering: For drainage and sewage treatment on construction sites, underground parking lots and underground facilities.
Water supply system: Vertical pumps are often used in urban water supply systems to pump water from water sources or water storage tanks into the water supply network to ensure the supply of water for residential, industrial and commercial purposes.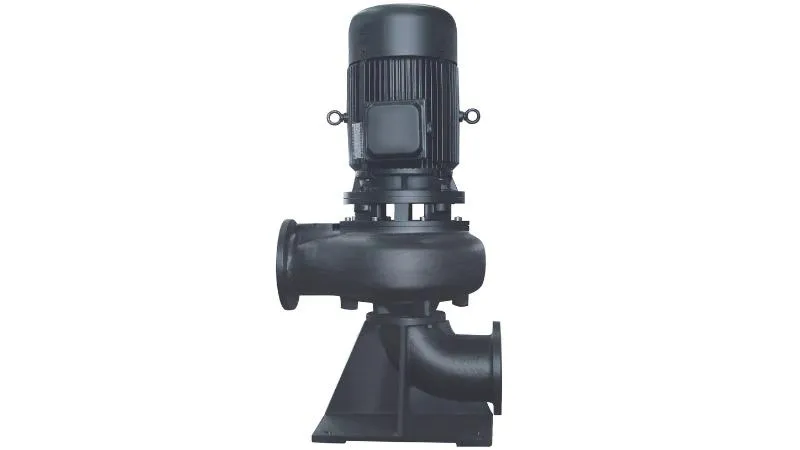
Drainage system: In urban drainage systems, vertical pumps are used to pump rainwater and sewage from low-lying areas or sewage pipes to ensure the smooth and normal operation of the drainage system.
Cooling Systems: During the cooling of industrial and commercial equipment, vertical pumps are used to pump coolant into the cooling equipment to help maintain the equipment's proper operating temperature.
Chemical process: In chemical production, vertical pumps are used to transport various chemical liquids, such as acids, alkalis, solvents, etc., to meet the needs of the production process.
Sewage treatment: Vertical pumps play an important role in sewage treatment plants, pumping sewage from ponds or sewage pipes to treatment equipment, and then discharging or recycling the treated water.
Mine Drainage: In mining and tunneling, vertical pumps are used to remove groundwater to keep the work area dry.
Construction Engineering: On construction sites, underground car parks and underground installations, vertical pumps are used for water drainage and pumping of concrete and liquid materials.
Marine Applications: Vertical pumps are used in marine engineering such as deep sea drainage, offshore oil field extraction and subsea pipeline installation.
Research the Market: Before choosing a manufacturer, do market research to know about the presence and product range of different manufacturers. Find and compare multiple manufacturers, including their reputation, product quality, and customer feedback.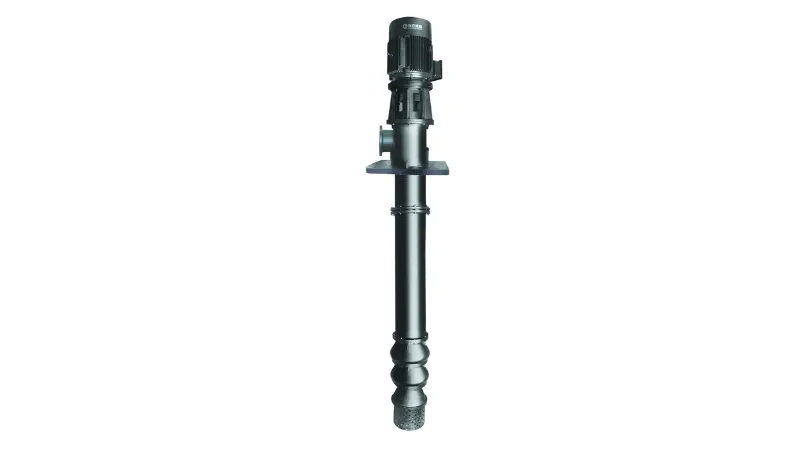
Clear product requirements: Determine your specific pump needs, including factors such as flow, head, liquid type, and operating environment. This helps you filter out manufacturers that fit your needs.
Quality and Certification: Make sure that the manufacturer's products meet international and industry standards and have the corresponding quality certification. Review the manufacturer's product documentation and certifications to ensure the quality and safety of their products.
Experience and Reputation: Choose a manufacturer with extensive experience and a good reputation. Look for the manufacturer's history and their success with similar projects.
Technical support and after-sales service: Find out whether the manufacturer provides good technical support and after-sales service. This includes repairs, parts supply and emergency support.
Cost and Budget: Consider your budgetary constraints, but don't let price alone be the only decision factor. Quality pump equipment usually requires a higher investment, but can save maintenance and operating costs in the long run.
Communication with Manufacturers: Communicate with potential manufacturers to ask questions and address concerns to ensure they can meet your needs and provide customized solutions.
References and Recommendations: Seek advice and referrals from peers, industry experts or other clients. Their experience can help you find a manufacturer you can trust.
Understand the warranty policy: Learn more about the manufacturer's product warranty policy, including warranty duration, coverage, and repair procedures.
Compare multiple sources: Finally, don’t rush into making a decision. Talk to multiple manufacturers, compare options, and make an informed choice based on your needs and budget.
Vertical pumps are indispensable equipment in the industrial and municipal sectors, and their versatility and adaptability allow them to play a key role in a variety of applications. From suspended vertical pumps to mixed flow vertical pumps, different types of pumps meet the needs of different engineering projects. I hope the information provided in this article can expand your understanding of vertical pumps . If you need to find a reliable vertical pump manufacturer, please feel free to contact LIANCHENG!
.png)

