

In the fields of liquid transfer and fluid mechanics, a pump is a critical piece of engineering equipment used to move liquids from one place to another. Among them, Mixed Flow pump and Axial Flow pump are two common types of pumps, and there are significant differences in their design and working principle. This article will focus on these two types of pumps to gain insight into their differences to meet specific liquid transfer needs.
A mixed flow pump is a device that transports and pressurizes liquid through rotating blades. It is a type of centrifugal pump, but it is different from traditional radial and axial flow pumps in design. The working principle of the mixed flow pump is to make the liquid have both radial and axial flow characteristics, so it is called "mixed flow". It is characterized by:
Flow direction: The fluid of the mixed flow pump flows in both the radial direction and the axial direction, which makes it suitable for a wide range of engineering applications.
Design structure: A mixed flow pump usually consists of a rotating impeller and a fixed guide vane ring. The liquid is sucked into the impeller, and under the action of the rotation of the impeller, it generates a rotational motion, and then is pushed into the guide vane ring, and finally enters the outlet pipe.
Applications: Mixed flow pumps are often used in applications requiring medium to high head and medium flow, such as irrigation systems, urban water supply, industrial processing and cooling systems, etc.
Energy Efficiency: Mixed flow pumps generally have high efficiency, which can save energy to a certain extent.
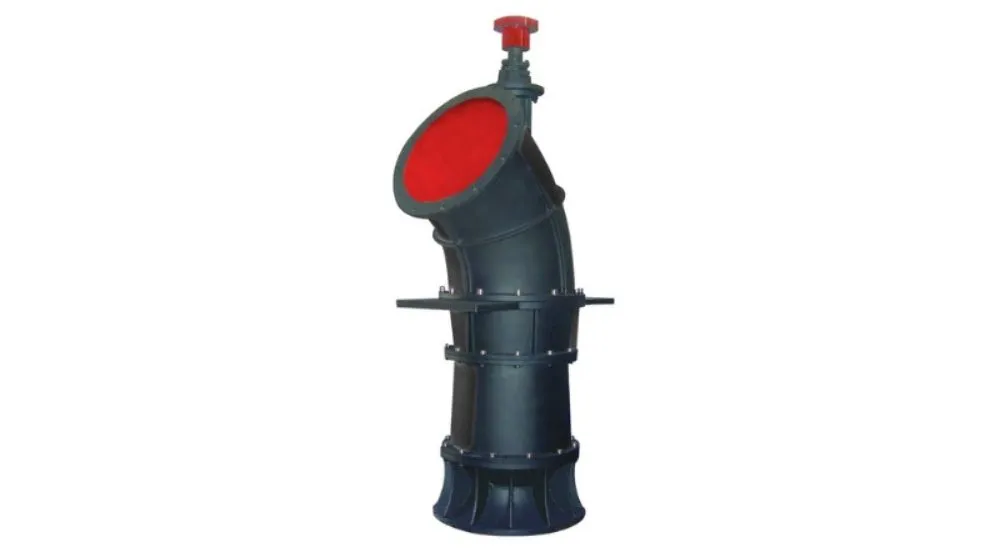

When the mixed flow pump starts to work, the liquid is first drawn into the inlet of the pump and enters the suction side of the impeller. The suction side is usually located in the center of the pump.
The impeller is the key component of the mixed flow pump, which is located in the center of the pump and is driven to rotate by a motor or other power source. After the liquid enters the impeller, the rotation of the impeller generates centrifugal force and rotational kinetic energy, pushing the liquid to the outer edge of the impeller.
Under the action of the rotation of the impeller, the liquid is accelerated and forms a vortex along the outer edge of the impeller. This vortex makes the liquid have radial and axial flow characteristics, that is, the liquid rotates in the impeller and flows in the axial direction at the same time.
The guide vane ring located on the outer edge of the impeller guides and restricts the flow of liquid. The guide vane ring guides the liquid away from the outlet side of the impeller and towards the outlet pipe.
After the action of the impeller and guide vane ring, the liquid is pushed to the outlet pipe of the mixed flow pump, and then enters the conveying system or process flow.
Radial and axial flow: The mixed flow pump is a pump that combines the characteristics of radial and axial flow. The liquid has both radial and axial flow in the impeller. This enables the mixed flow pump to adapt to the requirements of different flow angles and speeds.
Relatively low head
Mixed flow pumps are suitable for medium head requirements, and their heads are lower than some high head pumps. This makes it more suitable in some specific applications, such as water supply systems and cooling systems.
Medium flow
Mixed-flow pumps are suitable for medium-flow delivery, and their flow range is usually between centrifugal pumps and axial flow pumps. This makes it advantageous in some scenarios where flow and head need to be balanced.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Mixed flow pumps generally have high efficiency, which saves energy when transferring liquids. Its high energy efficiency helps reduce operating costs.
Relatively simple structure
The structure of the mixed flow pump is relatively simple, consisting of a rotating impeller and a fixed guide vane ring. This makes it relatively easy to manufacture, maintain and repair.
Fluid handling capacity
Mixed flow pumps are suitable for handling some liquids containing suspended matter, but their handling capacity may be lower than that of some specially designed pumps.
Mixed flow pumps are often used in urban water supply systems to transport water from water sources or water treatment plants to residential, industrial or commercial areas. Its medium head and flow characteristics are suitable for most urban water supply needs.
In industrial production process, cooling medium (such as water or other liquid) needs to be delivered to production equipment to cool process or equipment. Mixed flow pumps can be used in cooling systems to efficiently distribute the cooling medium to different devices or areas.
In the field of agriculture, water needs to be transported to the farmland for irrigation to meet the growth needs of crops. Mixed flow pumps are used in irrigation systems to efficiently move water from source to field.
Mixed flow pumps are used to transport and process liquids in some industrial processes, such as chemical production, textile industry, paper industry, etc. Its medium flow and head are suitable for different needs of industrial processing.
In the sewage treatment system, the mixed flow pump can be used to transport the sewage from the collection tank or treatment tank to the treatment equipment for treatment and purification.
On construction sites or buildings, mixed flow pumps can be used for drainage tasks, removing rainwater or waste water from basements or underground passages.
Mixed-flow pumps are also used in some energy production fields, such as in hydropower stations for transporting water to drive hydroelectric generators.
Mixed flow pumps are used in some ships as part of the propulsion system to move the water forward.
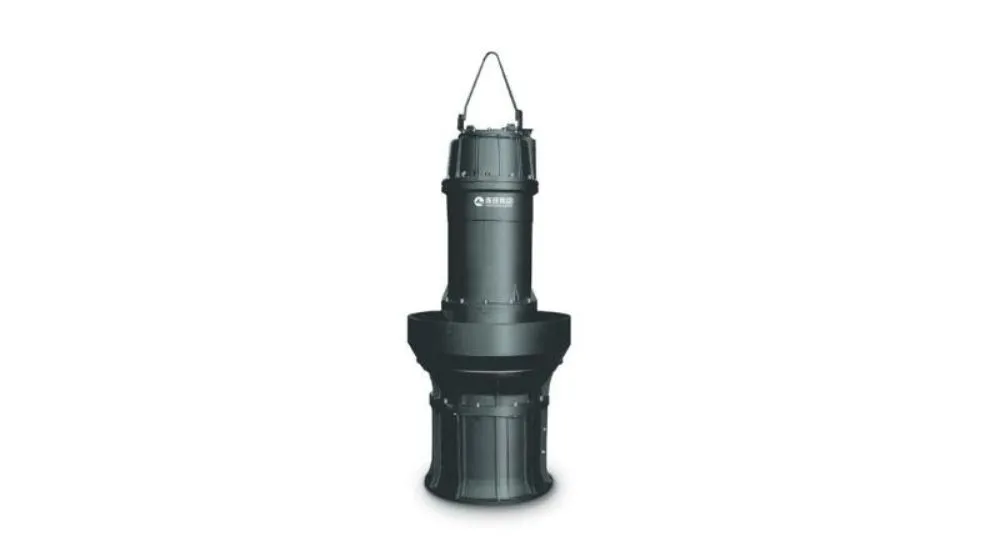

Impeller (rotor) of a mixed flow pump: The impeller is one of the most critical components in a mixed flow pump. It is located inside the pump and consists of multiple blades that rotate around an axis. The rotation of the impeller generates centrifugal force and rotational kinetic energy, which pushes the liquid to the outer edge of the impeller, so that the liquid has both radial and axial flow.
Guide vane ring (stator): The guide vane ring is located on the outer edge of the impeller, which is a fixed ring structure used to guide and limit the direction of liquid flow. The design of the guide vane ring can affect the flow angle and velocity of the liquid, thereby adjusting the performance of the mixed flow pump.
Pump Casing: The pump casing is the outer casing of the mixed flow pump and is used to enclose and protect the impeller and guide vane ring. The design of the pump casing often affects the flow path and pressure distribution of the liquid.
Bearings and Seals: Bearings are used to support the rotation of the impeller and ensure smooth operation of the pump. At the same time, the sealing system is used to prevent liquid leakage and external impurities from entering.
Axial flow pump is a common liquid conveying equipment, and its working principle is to realize conveying and boosting by liquid flowing in the axial direction. Axial flow pumps are suitable for medium to high flow and relatively low head applications, such as water transfer, drainage, cooling, etc. It is characterized by:
Flow direction: In the axial flow pump, the liquid mainly flows in the axial direction in the impeller, which is different from the radial and axial compound flow of the mixed flow pump.
Impeller structure: The impeller of an axial flow pump usually consists of a set of curved blades. The design of the shape and angle of the blades affects the flow direction and speed of the liquid.
Fields of application: Axial flow pumps are suitable for scenarios with large flow and relatively low head, such as irrigation, water resource transportation, water treatment plants, cooling in industrial processes, etc.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption: Axial flow pumps are generally highly efficient, saving energy when transferring large volumes of liquid.
Relatively simple structure: The structure of the axial flow pump is relatively simple, usually including impeller, pump casing and drive system, which makes its manufacture and maintenance relatively easy.
When an axial flow pump is started, liquid is drawn into the inlet of the pump and into the suction side of the impeller. The suction side is usually located in the center of the pump.
The impeller is the core component of an axial flow pump, consisting of multiple curved blades that rotate around an axis. After the liquid enters the impeller, the rotation of the impeller creates a helical-like motion that pushes the liquid in the axial direction towards the outlet side of the impeller.
The rotation of the impeller makes the liquid generate a certain driving force, so that the liquid passes through the impeller in an axial flow. The liquid is accelerated under the action of the impeller blades while advancing in the axial direction.
The liquid enters the pump casing after leaving the impeller, and the pump casing plays the role of guiding and restricting the flow of liquid. The design of the pump casing can affect the flow path and pressure distribution of the liquid.
Through the action of the impeller and the pump casing, the liquid is pushed to the outlet pipe of the axial flow pump, and then enters the delivery system or process flow.

Axial Flow
The main characteristic of an axial flow pump is that the liquid flows in an axial direction within the impeller. After the liquid enters the pump, it is pushed to flow along the axial direction by the rotation of the impeller, so that the liquid does not have obvious radial flow in the pump.
High Flow, Low Head
Axial flow pumps are suitable for high flow and relatively low head applications. It can efficiently transfer large volumes of liquid, but may be less efficient at higher heads.
Liquid Velocity
The liquid velocity in an axial flow pump is high due to the liquid flowing in the axial direction. This gives axial flow pumps an advantage in applications that need to move liquids quickly.
Stability of liquid flow
Since the liquid mainly flows along the axial direction, the liquid flow of the axial flow pump is relatively stable without causing obvious vortex or turbulent flow.
Efficiency and energy consumption
Axial flow pumps generally have high efficiency within the applicable flow and head range. However, as head increases, efficiency may decrease.
Relatively simple structure
The structure of the axial flow pump is relatively simple, mainly composed of impeller, pump casing and drive system, making it relatively easy to manufacture and maintain.
Axial flow pumps are suitable for irrigation systems in the agricultural field, which can transport water from water sources (such as rivers and lakes) to farmland to meet the irrigation needs of crops.
In construction sites, underground passages, underground garages and other places, axial flow pumps can be used for drainage to discharge accumulated water and maintain a dry environment.
Axial flow pumps can be used in urban water supply systems to transport water from water treatment plants to residential areas, commercial areas and industrial areas to ensure urban water supply.
In the industrial production process, the axial flow pump can deliver the cooling medium (such as water) to the equipment or process for cooling and maintain the normal operating temperature of the equipment.
Axial flow pumps are used in water treatment plants to pump raw water from sedimentation tanks or coagulation tanks into subsequent purification and treatment processes.
Axial flow pumps are used in hydroelectric power plants to pump water from downstream to upstream to provide driving force for hydroelectric generators.
In sewage treatment plants, axial flow pumps can transport sewage from collection tanks to treatment equipment for further purification and treatment.
In farms, axial flow pumps can be used to regulate the water level and water quality in aquaculture ponds to provide a suitable growth environment.
Axial flow pump propulsion system, also known as axial flow turbine propulsion system, is a technology that applies axial flow pump to ship propulsion. This system uses the fluid dynamics principle of the axial flow pump to introduce water flow into the axial flow pump, and generate propulsion through the rotation of the impeller, thereby pushing the ship forward.
The main components of an axial flow pump propulsion system include:
Axial flow pump: In the axial flow pump propulsion system, the axial flow pump, as the core component of the propulsion device, is responsible for passing the water flow through the impeller to generate propulsion.
Propeller (Impeller): The propeller is the part of the impeller in the propulsion system of the axial flow pump, which generates propulsion through rotation and propels the ship forward. A propeller typically consists of multiple blades whose shape and angle are designed to affect propulsion efficiency and performance.
Transmission system: The transmission system transmits the power of the engine to the impeller of the axial flow pump, which drives the impeller to rotate, thereby generating propulsion.
Hull installation: The axial flow pump propulsion system needs to be installed on the hull part of the ship to ensure that the propeller can enter the water smoothly and generate propulsion.

Working principle:
Mixed-flow pump: A mixed-flow pump is a pump that moves a liquid through the rotation of an impeller to increase the pressure. It pushes the fluid both axially and radially, causing the fluid to exit at an angle. Mixed flow pumps are usually suitable for medium head and medium flow.
Axial flow pump: Axial flow pump is a pump that expels fluid mainly by axial thrust. Its impeller shape and working principle make the fluid flow mainly along the pump axis, which is suitable for large flow and low lift.
Features:
Mixed-flow pump: The mixed-flow pump is suitable for medium head and flow, and its performance curve is relatively stable. In some cases, mixed flow pumps may have certain adaptability, but for higher head requirements, they may not be suitable.
Axial flow pump: Axial flow pump is suitable for large flow and low head, and its performance curve is relatively steep. It has advantages when large volumes of fluid transfer are required, but may not be as effective as other types of pumps in high head situations.
Application fields:
Mixed flow pump: Commonly used in water supply, drainage, cooling systems and other medium head and flow applications, such as urban water supply, industrial water, etc.
Axial flow pump: Commonly used in large-scale drainage projects, farmland irrigation, sewage treatment and other applications that need to handle a large amount of fluid.
Impeller Design:
Mixed-flow pump: The impeller design of the mixed-flow pump allows it to generate both axial and radial flow, so the design needs to consider how to balance these two flows. The impeller usually has more blades to ensure higher efficiency and pressure rise.
Axial Flow Pumps: Axial flow pumps have impellers designed to generate primarily axial flow. The blades are usually fewer and flatter in shape to minimize fluid resistance for high flow rates.
Head-flow characteristics:
Mixed Flow Pumps: Mixed flow pumps are usually designed to provide medium to high heads while providing moderate flow. Its performance curve is relatively stable, and the change of head and flow will not fluctuate significantly within a certain range.
Axial Flow Pumps: Axial flow pumps are designed to provide very high flow rates at low heads. However, in the case of higher head, the flow rate will be relatively reduced, and the performance curve will be steeper.
Scope of application:
Mixed Flow Pumps: Due to their ability to balance axial and radial flows to a certain extent, mixed flow pumps are suitable for medium flow and head situations, such as water supply and industrial use.
Axial flow pump: Axial flow pump is suitable for situations that require large flow but low head, such as farmland irrigation, drainage projects, etc.
Installation arrangement:
Mixed-flow pumps: Since mixed-flow pumps are designed with both axial and radial flow in mind, they typically require smaller inlet and outlet sizes and are suitable for installation in smaller spaces.
Axial Flow Pumps: Axial flow pumps generally require larger inlet and outlet sizes to accommodate the large volumes of fluid flowing through them. Its mounting arrangement may require more space.
As two important branches of centrifugal pumps, Mixed Flow pump and Axial Flow pump have their own unique advantages and scope of application in the field of liquid delivery. In LIANCHENG, we can provide you with good products and services. We have more than 30 years of industry experience and are one of the largest pump manufacturers and suppliers in China. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact LIANCHENG.
.png)

