

Table of contents:
Chemical pumps are an important class of equipment widely used in industry and laboratories, and they play a key role in many processes. These pumps are designed to transfer a wide variety of chemical liquids, including corrosive liquids, organic solvents, high-purity chemicals, and liquids with special properties. Let's take a closer look at chemical pumps .
A chemical pump is a mechanical device used to transport chemical liquids or substances. They are widely used in chemical, oil and gas, pharmaceutical, sewage treatment and other industrial fields, as well as laboratories and scientific research institutions. The design and material selection of chemical pumps usually take into account the characteristics of chemical liquids, such as corrosiveness, viscosity and temperature, etc., to ensure their stable and efficient operation in specific chemical processes.
A chemical pump typically consists of one or more pump heads, drives, seals and piping. A pump head is the part responsible for pumping or pushing a chemical liquid from one place to another. The drive means can be electric motor, pneumatically driven or manually operated to provide the required power. The sealing device is to prevent the pump from leaking during operation, so as to ensure the safety of operation and the protection of the environment.
Ensure safety: Since the chemical liquids handled may be corrosive, toxic or flammable, chemical pumps are designed and sealed to ensure that the liquid will not leak during the transfer process, thus ensuring the safety of operators and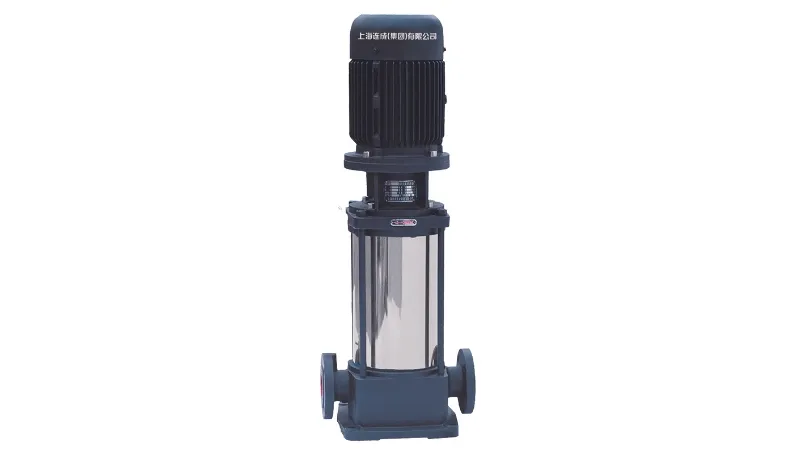 the environment.
the environment.
Increased production efficiency: Chemical pumps can deliver chemical liquids quickly and steadily, thereby increasing production efficiency, reducing downtime, and reducing costs.
Precise control: Chemical pumps can achieve precise control of parameters such as liquid flow, pressure and mixing ratio, ensuring the accuracy and stability of chemical processes.
Strong adaptability: The design and material selection of chemical pumps can adapt to the characteristics of different chemical liquids, so that they can operate reliably in various complex chemical processes.
A chemical pump is a device that converts chemical energy into mechanical energy to drive fluid flow. Its working principle involves the process in which the product of a chemical reaction pushes a liquid. Here is a brief description of how a chemical pump works:
Chemical Reaction: A chemical pump contains one or more chemical substances that produce a chemical reaction. These chemicals can react chemically under certain conditions to produce gases, heat or other products.
Product push: The product of a chemical reaction is usually a gas. These products create high pressure inside the pump and gradually push the liquid forward.
Pushing Liquid: Liquid is pushed into the outlet of the pump due to the increased pressure of the product. In this way, the liquid is gradually expelled along the flow path of the pump.
Cycle process: The work of the chemical pump is a cycle process. As the chemical reaction continues, the product builds up, keeping the liquid moving.
Chemical pumps are often used in special applications, such as when there is no power supply, or where liquid delivery under specific conditions is required. However, they usually need to be well sealed to avoid leakage of harmful gases, and they need to pay attention to safety and environmental protection during use
Chemical reaction push: Unlike traditional mechanical pumps, chemical pumps push liquids through chemical reactions that produce gases or products. This special working principle makes chemical pumps suitable for some special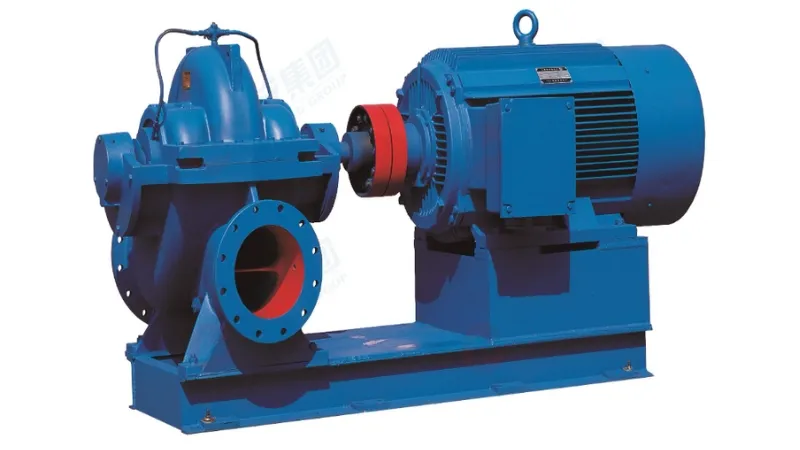 scenarios.
scenarios.
No electricity needed: Since the chemical pump is powered by a chemical reaction, no external power supply is required. This makes chemical pumps useful in some environments where electricity is not available or accessible.
Self-priming function: Chemical pumps usually have good self-priming ability, which can draw liquid from a low place to a certain extent and push it to a high place. This makes chemical pumps excellent in certain applications where liquid lifting is required.
High Corrosion Resistance: Because the liquid parts of chemical pumps are often in direct contact with the products of chemical reactions, they are usually constructed of highly corrosion-resistant materials to prevent damage.
Applicable to special liquids: Some liquids may corrode or pollute traditional mechanical pump materials, while chemical pumps are suitable for some special liquids, such as strong acids and alkalis, due to their strong corrosion resistance.
Precise control: The flow rate of the chemical pump can be precisely controlled by adjusting the conditions of the chemical reaction, making it superior in some applications that require precise flow control.
Wide range of applications: chemical pumps are widely used in chemical industry, laboratory, environmental protection, metallurgy and other fields, and play a key role in scenarios that require no power supply, strong corrosion resistance, and special liquid delivery.
Centrifugal pumps: Centrifugal pumps are a common mechanical pump, but they can also be used to handle some special liquids, for example in the chemical industry.
Gas push pump: This type of chemical pump uses the gas generated by chemical reactions to push the liquid to flow. Common gas push pumps include air pumps and compressed air pumps.
Liquid push pump: This type of chemical pump uses the driving force of the liquid itself to achieve liquid delivery by changing the pressure or flow rate of the liquid. For example, positive displacement pumps and plunger pumps, etc.
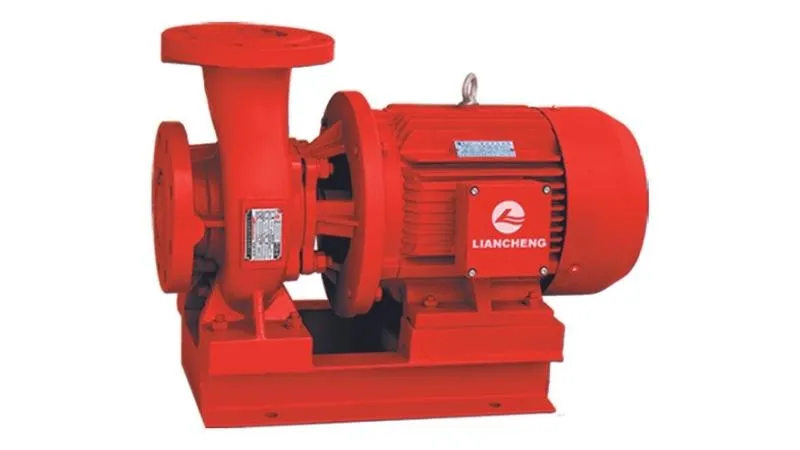
Magnetic pump: The magnetic pump drives the liquid movement through the magnetic field generated by electromagnetic induction, avoiding the mechanical shaft seal, and is suitable for handling volatile and highly corrosive liquids.
Diaphragm pump: The diaphragm pump pushes the liquid through the contraction and expansion of the diaphragm, which is suitable for conveying volatile, corrosive or granular liquids.
Screw pump: The screw pump uses the rotation of the screw to push the liquid, which is suitable for high-viscosity liquids and liquids containing solid particles.
Pneumatic Diaphragm Pump: Pneumatic diaphragm pump is a pump that pushes liquid through the contraction and expansion of the pneumatically driven diaphragm, which is suitable for special liquids and volatile liquids.
Jet pumps: Jet pumps use the kinetic energy of a high-velocity fluid to create a negative pressure that draws the liquid in and expels it through an airflow that propels the liquid.

Stainless steel
plastic
ceramics
fluororubber
Tantalum
nickel alloy
composite material
choose the right material
good sealing performance
Consider pump discharge
flow and head
Automatic control and monitoring system
temperature and pressure
Anti-clogging design
Leakage and Failure Prevention
Ease of maintenance and maintenance
Compliance with standards and regulations
Chemical Industry
The chemical industry is one of the main fields of application for chemical pumps. Chemical pumps are used in the chemical production process to transport various chemical liquids, such as acids, alkalis, solutions, solvents, etc. They play a key role in chemical reaction, mixing, transfer and storage, ensuring stable production and quality control of chemical products.
Oil and Gas Industry
During oil and gas exploration, extraction, refining, and transportation, chemical pumps are used to process crude oil, petroleum products, and chemical additives, among others. They ensure the safe and efficient transfer and processing of oil and gas, and are used to increase the production of oil wells and maintain equipment.
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry places high demands on the accurate delivery and mixing of products. Chemical pumps are used in the pharmaceutical process to transport pharmaceutical raw materials, additives and reactants, ensuring precise dosing and production efficiency of pharmaceuticals while meeting stringent quality control requirements.
Sewage treatment industry
In the process of sewage treatment, chemical pumps are used to add chemical reagents, treatment agents or agitators to remove pollutants in sewage, improve water quality and protect the environment. Chemical pumps are often used in stirring tanks, sedimentation tanks and sedimentation tanks in sewage treatment plants.
Other fields of application
Chemical pumps are used in scientific research experiments and laboratories for accurate delivery and mixing of experimental liquids, as well as automatic control during experiments.
Flow and head essentials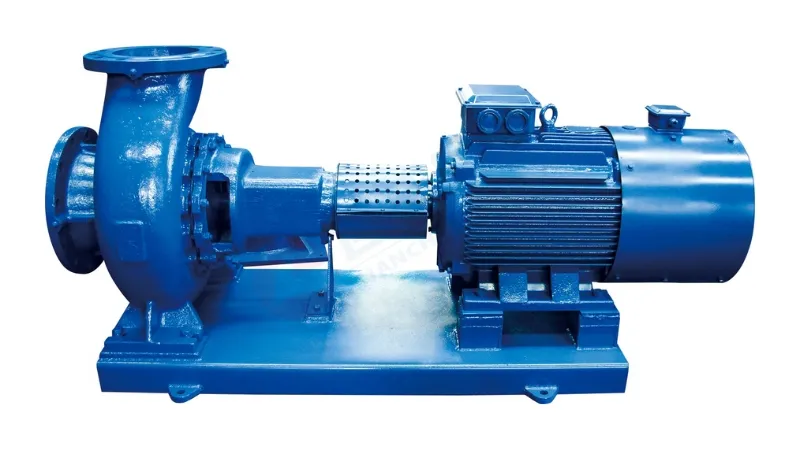
The flow rate of a chemical pump refers to the volume of liquid delivered per unit time, usually in liters per second or cubic meters per hour. Select the appropriate flow range according to process requirements and liquid delivery volume. Head is the vertical height over which the liquid is being pumped, usually measured in meters. Choose the appropriate head according to the destination and height difference of the liquid to be transported.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
Temperature limitations: Chemical pumps must take into account the temperature range of the liquids they are handling during operation. Chemical pumps of different materials have different limitations in the temperature they can withstand. High temperatures can cause deformation, expansion or damage to pump materials, so it is important to ensure that the chemical pump selected is suitable for the operating temperature range of the liquid. Also, low temperature conditions may cause the liquid to freeze or the sealing performance of the pump to deteriorate, so it is necessary to ensure that the pump can operate stably in a low temperature environment.
Pressure limitations: Chemical pumps need to be designed and used with the maximum required working pressure in mind. The construction and materials of the pump must be able to withstand the highest pressures of the liquids handled. Exceeding the pressure range of the pump may cause the pump to fail, leak or rupture, which will pose a serious safety hazard.
In order to ensure the normal operation and safety of chemical pumps, operators should strictly abide by the following measures:
Make sure that the pump materials and seals are suitable for the operating temperature and pressure range of the liquid.
Regularly check the operating temperature and pressure of the pump to ensure it is operating within a safe range.
Avoid exceeding the maximum allowable pressure of the pump to prevent pump damage or hazardous conditions.
When using the pump in a high or low temperature environment, pay attention to take necessary heat preservation or antifreeze measures to ensure the normal operation of the pump.
In the case of large changes in liquid temperature or pressure, choose a chemical pump with higher temperature and pressure adaptability.
Chemical pump performance
The performance of chemical pumps is affected by many factors such as flow rate, head, pressure, temperature range, material selection, self-priming capacity, energy-saving performance, reliability and maintainability. According to the specific process requirements and liquid characteristics, selecting the appropriate chemical pump is the key to ensure the stable and efficient operation of the process.
Choose the Chemical Pump That Fits Your Needs
Determine the application requirements: First, clarify the application scenarios and work requirements of the chemical pump, including the required parameters such as flow rate, head, temperature range, pressure and conveying medium.
Consider the characteristics of the liquid: understand the characteristics of the liquid being processed, such as corrosiveness, viscosity, solid content and temperature, and choose the pump material and sealing method suitable for the liquid characteristics.
Material selection: According to the characteristics of the liquid, select corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant and high-temperature-resistant chemical pump materials to ensure that the pump can run stably under the action of the liquid.
Self-priming ability: For scenarios that need to work at high places or away from liquid sources, choose a chemical pump with good self-priming ability to ensure the convenience of starting and operation.
Consider the reliability of the pump: choose a chemical pump with high reliability, reduce maintenance and downtime, and improve the continuity and stability of industrial production.
Energy-saving performance: Some chemical pumps are equipped with energy-saving technology. Choosing a pump with energy-saving performance can reduce energy consumption and improve work efficiency.
Safety and environmental protection: consider the sealing performance and leakage protection measures of the pump to ensure safe operation and meet environmental protection standards.
Economy: Considering performance, quality and price comprehensively, choose a chemical pump with high cost performance to meet budget and engineering requirements.
Consult a professional: If necessary, it is recommended to consult a professional chemical pump supplier or engineer for more detailed suggestions and solutions.
Daily maintenance points
The daily maintenance of chemical pumps is very important, mainly including the following points: regular cleaning and lubrication, checking the sealing state, thoroughly cleaning the liquid, maintaining an appropriate liquid level, regular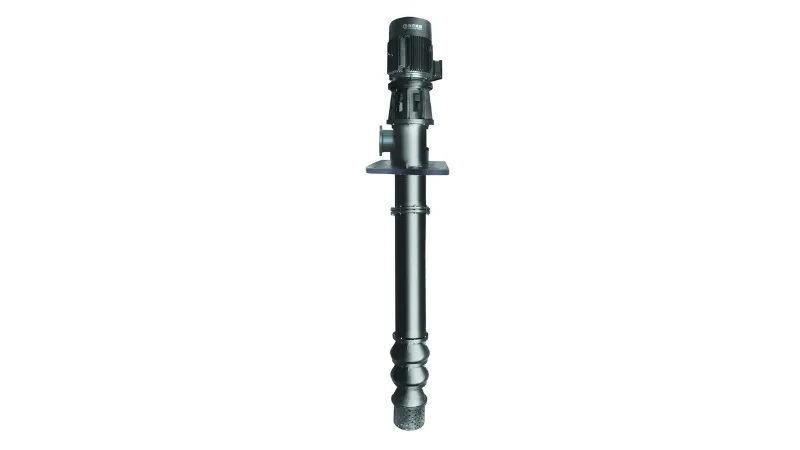 maintenance and maintenance, paying attention to the operating status, clear and visible warning signs, training operators, Use durable accessories and have them checked regularly by a professional technician. Proper maintenance of chemical pumps can help prolong life, improve efficiency and ensure safe operation.
maintenance and maintenance, paying attention to the operating status, clear and visible warning signs, training operators, Use durable accessories and have them checked regularly by a professional technician. Proper maintenance of chemical pumps can help prolong life, improve efficiency and ensure safe operation.
Common faults and their troubleshooting methods
Leakage problem:
Causes of failure: damage to pump body seals, aging of packing seals, failure of mechanical seals, etc.
Remedy: replace the damaged seal, repair or replace the mechanical seal.
Pump does not start or starts with difficulty:
Causes of failure: power failure, motor damage, circuit problems, etc.
Remedy: Check whether the power supply is energized, check the motor and circuit, and repair or replace the faulty parts in time.
Low flow or low head:
Cause of failure: The liquid inlet or outlet of the pump is blocked, the impeller is damaged, the pump is not tightly sealed, etc.
Remedy: Clean the liquid inlet and outlet, replace the damaged impeller, adjust or replace the seal of the pump.
Unusual noise or vibration:
Causes of failure: loose internal parts of the pump, damaged bearings, unbalanced or misaligned problems.
Remedy: Check the parts of the pump, fasten loose parts, replace damaged bearings, balance or adjust the alignment.
Pump running erratically:
Causes of failure: unstable power supply, liquid level change at the inlet, damage to the impeller of the pump, etc.
Remedy: Check the stability of the power supply, keep the liquid level at the liquid inlet stable, and replace the damaged impeller.
Temperature is too high:
Cause of failure: too much heat generated by internal friction of the pump, the liquid temperature is too high, etc.
Remedy: Check the lubrication of the pump, ensure good lubrication and cooling, and reduce the liquid temperature.
Poor self-priming effect:
Cause of failure: air leakage in the liquid inlet pipe, poor sealing of the pump, etc.
Remedy: Check whether the inlet pipe is well sealed, repair or replace the seal of the pump.
Motor overheating:
Cause of failure: The motor load is too heavy, the power supply is unstable, etc.
Remedy: reduce the motor load and check the stability of the power supply.
Safety Precautions
Read the operation manual carefully: Before using the chemical pump, be sure to read and understand the operation manual and safety instructions of the chemical pump carefully, and be familiar with the use method and precautions of the pump.
Wear Personal Protective Equipment: When operating the chemical pump, appropriate personal protective equipment such as safety glasses, gloves, face shield, etc. should be worn to prevent splashing of liquids or inhalation of harmful gases.
Maintain good ventilation: When using chemical pumps, ensure that the operating area is well ventilated to avoid the accumulation of harmful gases.
Avoid idling: Before starting the chemical pump, make sure the pump body is filled with liquid and avoid idling, so as not to damage the pump or cause other safety hazards.
Regular maintenance: Regular maintenance and inspection of chemical pumps to keep the pumps in good condition and prevent breakdowns and leaks.
Pay attention to the nature of the liquid: understand the nature of the liquid being handled, especially its corrosiveness, toxicity and volatility, and take corresponding safety measures.
Power failure and emergency situation: In case of emergency, the power supply should be cut off immediately, the operation of the chemical pump should be stopped, and corresponding emergency measures should be taken.
Unauthorized modification is prohibited: It is strictly forbidden to modify the chemical pump or remove the safety device without authorization to ensure the safety and reliability of the pump.
Storing liquids: When storing chemicals, follow appropriate storage regulations and keep liquids in a safe place away from sources of fire and heat.
Learn first aid measures: Operators should learn basic first aid measures to deal with emergencies.
Chemical pumps play an indispensable role in modern industry and laboratories. They are used in a wide range of applications and provide reliable solutions for many special liquid handling and chemical reactions. If you need to know more about chemical pumps, please feel free to contact LIANCHENG!
.png)

