

Whether in industry, construction or urban infrastructure, pumps are a key piece of equipment that plays an important role in transporting liquids from one point to another. In the world of pumps, axial flow pumps and centrifugal pumps are two common types with unique characteristics. Their different working principles, fields of application, and advantages and disadvantages make it necessary to carefully weigh various factors when selecting a suitable pump to ensure the best performance and effect.
Table of contents:
The liquid enters the pump body through the inlet of the axial flow pump. Inside an axial flow pump, the liquid interacts with the vanes (also known as vane wheels). The blades rotate to push the liquid in the axial direction. Under the action of the vanes, the liquid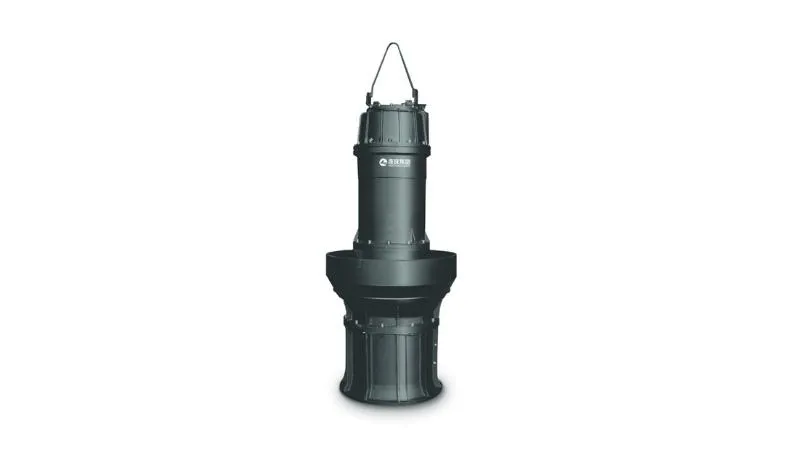 is gradually accelerated and flows along the axial direction. The design and direction of rotation of the blades determine the direction and speed of the liquid flow. As the liquid flows, due to the action of the blades, the kinetic energy of the liquid is converted into pressure energy, which gradually increases the pressure of the liquid. When the liquid reaches the highest pressure point, it is pushed to the outlet of the axial flow pump, and then discharged into the delivery pipe or other equipment.
is gradually accelerated and flows along the axial direction. The design and direction of rotation of the blades determine the direction and speed of the liquid flow. As the liquid flows, due to the action of the blades, the kinetic energy of the liquid is converted into pressure energy, which gradually increases the pressure of the liquid. When the liquid reaches the highest pressure point, it is pushed to the outlet of the axial flow pump, and then discharged into the delivery pipe or other equipment.
In fact, the axial flow pump accelerates and pushes the liquid from the inlet to the outlet through the rotation of the blades to realize the transportation of the liquid. This operating principle makes axial flow pumps particularly suitable for applications requiring high flow rates and low heads.
Pump body and volute: The pump body is the outer casing of the axial flow pump and houses the various components inside. The volute is a curved shell in the pump body that helps direct the flow of fluid, increasing pressure.
Blade wheel: The blade wheel is the core component of the axial flow pump, which is fixed on a rotating shaft by multiple blades. As the disc rotates, the interaction of the vanes and the fluid pushes the fluid in an axial direction.
Inlet port and outlet port: The inlet port is where the liquid enters the pump body, while the outlet port is where the liquid exits the pump body. These two ports are usually located at both ends of the pump body.
Bearings and Shafts: Bearings are used to support the rotation of the blade wheel and reduce the friction caused by the rotation. The shaft is the part that connects the blade wheel to the drive.
Sealing device: The axial flow pump needs to be sealed at the inlet and outlet to prevent liquid leakage. The sealing device can be a mechanical seal or a stuffing seal.
Drive unit: The drive unit transmits power to the blade wheel through the shaft, causing it to rotate. This could be an electric motor, engine, or other type of power source.
Support Structure: Pump bodies often require support structures to hold them in place. This could be a ground stand or another type of support.
Cooling and Lubrication System: During operation, axial flow pumps may generate heat and require a cooling system to maintain proper operating temperatures. Lubrication systems are used to keep rotating parts running smoothly.
High flow capacity: Axial flow pumps are suitable for situations where high flow rates are required. Their design allows a large amount of liquid to pass through the pump body in a short time.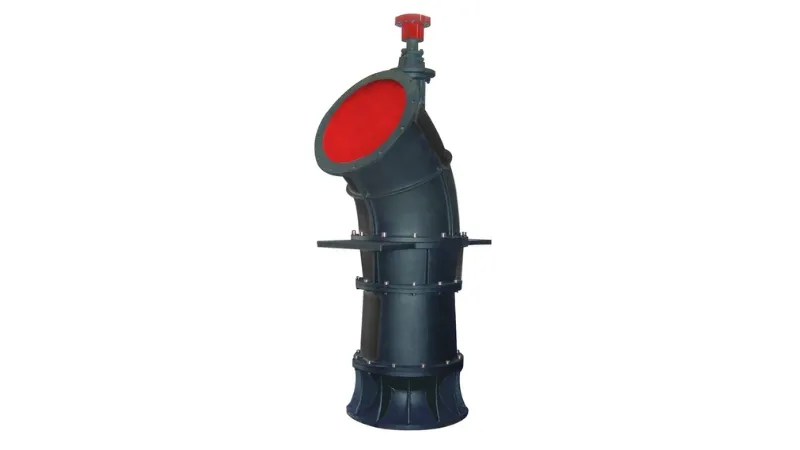
Lower head requirement: Compared with other types of pumps, axial flow pumps require a lower head, so they are suitable for scenarios where liquids need to be transported within a smaller height range.
High efficiency: Axial flow pumps usually have high efficiency because the liquid flows through the axial direction of the blade wheel, reducing the friction loss of the liquid.
Compact design: The design of the axial flow pump is relatively compact and takes up less space, making it suitable for limited installation spaces.
Strong adaptability: Axial flow pumps can be used for a variety of different liquids, including clean water, sewage, chemical liquids, etc., and have strong adaptability.
Easy maintenance: Due to its relatively simple structure, axial flow pumps are relatively easy to maintain and clean.
Adjustability: Some axial flow pumps have adjustable vane angles or adjustments that can be tuned according to actual needs for optimum performance.
Low noise levels: Axial flow pumps generally produce lower noise levels than some other pump types, which is an advantage for noise-sensitive applications.
Economy: The manufacturing and installation costs of axial flow pumps are relatively low, which is suitable for projects with high economic requirements.
Customizability: According to different application requirements, the axial flow pump can be customized according to parameters such as flow rate and head.
Agricultural irrigation: Axial flow pumps are suitable for water irrigation of large agricultural fields because of their ability to efficiently deliver large volumes of water.
Drainage systems: In drainage systems used to remove sewage, rainwater and other liquids, axial flow pumps can efficiently discharge liquids at low head.
Sewage Treatment Plants: During sewage treatment, axial flow pumps can help in the treatment and transfer of sewage by transporting it from different treatment stages to the next.
Cooling system: In industrial equipment and power plants, etc., axial flow pumps can be used in cooling systems to circulate cooling liquid to maintain the temperature of the equipment.
Ships and ports: Axial flow pumps can be used for loading and unloading cargo, cleaning ship hulls, and fresh water supply.
Environmental engineering: In environmental engineering projects such as wetland restoration, water body protection and flood control, axial flow pumps can regulate and manage water levels.
Mining industry: In terms of mine drainage and tailings treatment, axial flow pumps can handle a large amount of liquid and reduce the moisture content of ore.
Fresh water supply: In both urban and rural areas, axial flow pumps can be used to extract ground water or deliver water to water treatment plants.
Wind farms: Axial flow pumps can be used to cool the cooling systems of wind turbine generators.
Hydropower: In some small hydroelectric plants, axial flow pumps direct the flow of water to turbine generators, which generate electricity.
The liquid enters the pump body through the inlet of the centrifugal pump. Inside the pump body, the liquid interacts with the vane wheel. Bladed wheels consist of multiple blades fixed to a rotating shaft. As the vaned wheel rotates, the liquid creates a centrifugal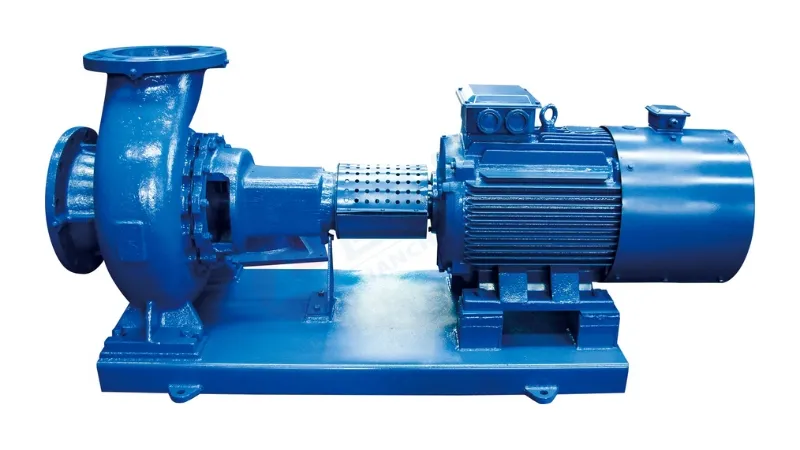 force due to the shape of the vanes and the speed at which they rotate. This gradually accelerates the liquid, increasing its kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of the liquid causes it to be pushed to the outlet of the centrifugal pump, where it is discharged into a pipe or other device. The liquid is continuously accelerated under the action of the vane wheel, and the kinetic energy is gradually converted into pressure energy, thereby increasing the pressure of the liquid.
force due to the shape of the vanes and the speed at which they rotate. This gradually accelerates the liquid, increasing its kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of the liquid causes it to be pushed to the outlet of the centrifugal pump, where it is discharged into a pipe or other device. The liquid is continuously accelerated under the action of the vane wheel, and the kinetic energy is gradually converted into pressure energy, thereby increasing the pressure of the liquid.
Casing and Volute: The outer casing of a centrifugal pump, called the casing, contains the key components inside. The volute is the curved shape of the shell within the pump body that helps direct the flow of fluid and build up pressure.
Blade wheel: One of the core components of a centrifugal pump, consisting of multiple blades fixed on a rotating shaft. The shape and number of blades in the wheel affect the flow of liquid and the generation of pressure.
Inlet and outlet ports: The inlet port is where the liquid enters the pump body, while the outlet port is where the liquid exits the pump body. These two ports are usually located at different locations on the pump body.
Bearings and Shafts: Bearings are used to support the rotation of the blade wheel and reduce drag due to friction. The shaft connects the blade wheel to the drive.
Sealing device: Centrifugal pumps need to be sealed at the inlet and outlet to prevent liquid leakage. Mechanical seals and packing seals are common sealing methods.
Drive unit: The drive unit transmits power to the blade wheel through the shaft, causing it to rotate. This could be an electric motor, engine or other power source.
Support Structure: Pump bodies often require support structures to hold them in place. This could be a ground stand or another type of support.
Cooling and Lubrication Systems: Centrifugal pumps generate heat when they operate, so cooling systems are often required to maintain proper operating temperatures. Lubrication systems are used to keep rotating parts functioning properly.
Valves and pipes: At the inlet and outlet, there are usually valves and pipes to control the flow of liquid and regulate the flow.
Wide range of applications: Centrifugal pumps are suitable for various liquids, including clean water, sewage, chemical liquids, etc., and have strong adaptability.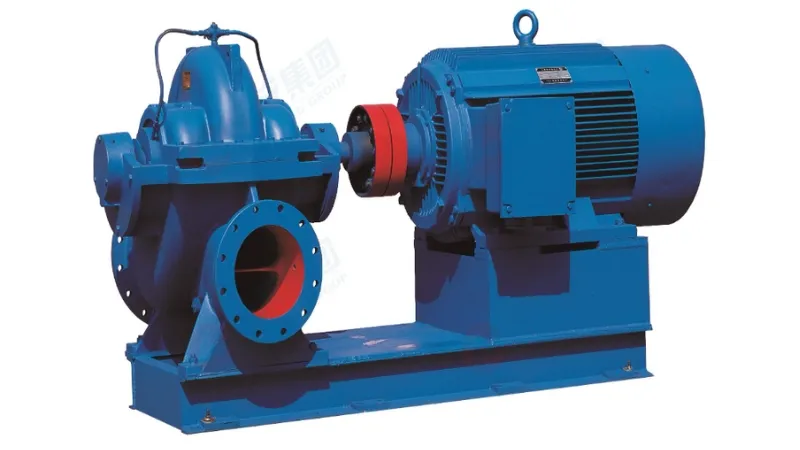
High Efficiency: Centrifugal pumps generally have high efficiency, which can effectively transport liquid to the desired location and reduce energy consumption.
Simple structure: The structure of the centrifugal pump is relatively simple, easy to manufacture, maintain and repair, and reduces operation and maintenance costs.
High Flow: Centrifugal pumps are suitable for high flow applications and can quickly transfer large volumes of liquid to the desired location.
Medium head: For medium head scenarios, centrifugal pumps do an excellent job of effectively lifting the liquid to the desired height.
Compact Design: Centrifugal pumps are relatively compact in design and take up less space, making them suitable for limited installation spaces.
Stability: Centrifugal pumps usually have relatively stable performance during operation, and can maintain relatively stable flow and pressure under different working conditions.
Multi-cascade use: Through multi-cascade use, the head and pressure of the centrifugal pump can be increased, which is suitable for scenarios that require a higher head.
Long-distance delivery: Centrifugal pumps are suitable for scenarios where liquids need to be delivered to long distances, such as urban water supply systems.
Quiet: Centrifugal pumps generally produce lower noise levels than some other pump types.
Construction engineering: Centrifugal pumps are used in building water supply, fire protection systems, drainage and sewage systems to ensure the flow of liquids inside and outside buildings.
Municipal water supply: Centrifugal pumps transport water from water sources to residential and industrial water sources in urban water supply systems to ensure the distribution of water resources.
Sewage treatment: Centrifugal pumps are used to pump sewage from low places to sewage treatment plants, and to transport liquids during treatment.
Industrial fields: Centrifugal pumps are used in liquid transportation, cooling systems, chemical production, raw material transportation, etc. in industrial processes.
Agricultural field: used for farmland irrigation, crop sprinkler irrigation systems, and liquid delivery needs of farms.
Oil and Gas: Centrifugal pumps are used for liquid handling and delivery during oil and gas exploration, production and delivery.
Food and beverage industry: for liquid food production, processing and delivery, such as juice, beverages, milk, etc.
Water Treatment: Centrifugal pumps are used to convey, mix and circulate liquids in the process of purifying, filtering and treating water.
Energy sector: In power stations, nuclear power plants and other energy industries, centrifugal pumps are used for cooling, liquid transfer and circulation.
Shipping and ports: Used in port facilities, ship loading and unloading and berth drainage to ensure normal port operations.
Fluid movement mode of axial flow pump:
The working principle of the axial flow pump is to push the liquid from the inlet to the outlet through the rotation of the blade wheel. The liquid flows in the axial direction, following the path of the pump shaft. The design of the blade wheel allows the liquid to be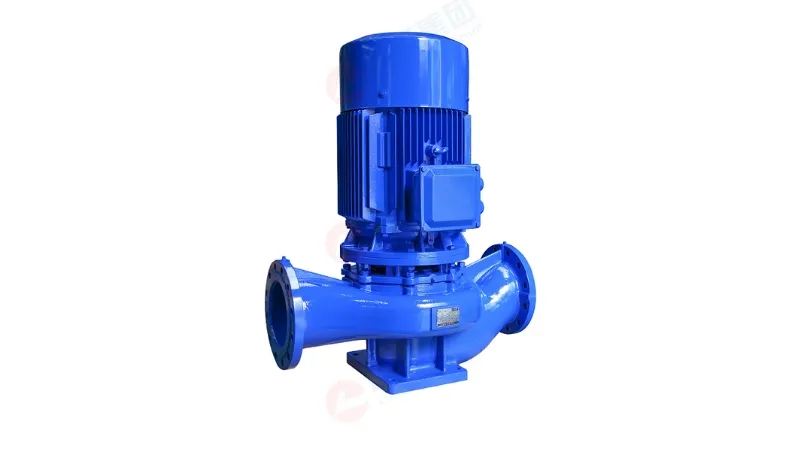 accelerated and pushed to the outlet, thereby realizing liquid transportation. The fluid motion of the axial flow pump is suitable for applications requiring high flow and low head. It produces a linear flow pattern in the fluid, similar to the flow of a river.
accelerated and pushed to the outlet, thereby realizing liquid transportation. The fluid motion of the axial flow pump is suitable for applications requiring high flow and low head. It produces a linear flow pattern in the fluid, similar to the flow of a river.
Fluid movement mode of centrifugal pump:
The working principle of the centrifugal pump is to push the liquid from the center to the outside by centrifugal force, and the liquid flows in the radial direction. After the liquid enters the pump body, it is forced to diffuse from the center outward by the centrifugal force of the vane wheel, forming a relatively uniform vortex flow. The fluid motion of centrifugal pumps is suitable for medium flow, medium head applications. It forms a vortex in the fluid, similar to the motion of a vortex.
Axial flow pump efficiency:
Axial flow pumps generally exhibit higher efficiencies at lower heads. Because the liquid flows in the axial direction, there is relatively little liquid friction and energy loss, making axial flow pumps highly efficient in high-flow, low-lift applications. However, the efficiency of an axial flow pump may decrease at higher heads because the liquid needs to overcome greater resistance and friction.
Centrifugal pump efficiency:
Centrifugal pumps generally exhibit higher efficiencies at medium to higher heads. Since the liquid flows in the radial direction, the centrifugal pump can better overcome the resistance of the liquid and is suitable for medium flow and medium head applications. Centrifugal pumps can produce high kinetic energy conversion efficiency during fluid flow, so they have good efficiency in many operating conditions.
Lift characteristics of axial flow pump:
Axial flow pumps are generally suitable for lower head ranges in terms of head characteristics. As the head increases, the flow rate of the axial flow pump will gradually decrease, because at higher head, the liquid needs to overcome more resistance and friction. Therefore, the head characteristic curve of the axial flow pump generally shows a relatively stable downward trend, which is suitable for applications requiring large flow and lower head.
Lift characteristics of centrifugal pump:
The head characteristics of centrifugal pumps usually show a curve that rises and then tends to be stable. When the head is low, the flow rate of the centrifugal pump is large, and the flow rate will gradually decrease with the increase of the head. However, within a certain range, the flow rate and head of a centrifugal pump will maintain a relatively stable relationship, making it suitable for scenarios with medium flow and medium head.
Axial flow pumps are suitable for large flow and low head situations. Its high flow capacity, low head requirements and high efficiency make it an excellent performer in scenarios where fast, high-volume liquid transfer is required. However, the application of axial flow pumps is limited by the lift range and is not suitable for higher lift requirements.
Centrifugal pumps have wide adaptability in applications with medium flow and medium head. Its strong adaptability, high efficiency and good stability make it superior in a variety of liquid delivery needs. However, centrifugal pumps may have insufficient flow at lower heads, and their more complex construction may require more maintenance and adjustments.
Determine application requirements: First, clarify the application's flow, head, liquid properties, temperature, pressure and other requirements. These factors will directly affect the type and specifications of the required pump.
Know how it works: Understand how different pump types work, such as axial and centrifugal pumps, to know which type is better for a particular application.
Consider flow and head: Depending on the flow and head requirements of the application, choose a pump type that will cover these ranges. Axial flow pumps are suitable for large flow and low head, while centrifugal pumps are suitable for medium flow and medium head.
Liquid Characteristics: Consider the characteristics of the liquid such as viscosity, corrosiveness, solid particle content, etc. to select a pump material and design that can handle the properties of the liquid.
Efficiency needs: Select a pump with the appropriate efficiency based on the energy efficiency requirements of the application. Consider the efficiency curve of the pump and its efficiency performance under the required operating conditions.
Space and Installation Requirements: Consider pump size and installation needs to ensure the pump can fit into existing space and equipment.
Maintenance and Service: Consider how easily the pump can be maintained, and how often repairs and maintenance will be required. Simple pumps are usually easier to maintain.
Cost: Consider the purchase cost, installation cost, operation cost and maintenance cost of the pump comprehensively, and choose the pump type that meets the budget.
Manufacturer reputation: Choose a reputable pump manufacturer to ensure product quality and after-sales service.
Professional Consultation: If unsure about pump selection, a professional engineer or pump supplier can be consulted for application-specific advice.
In the field of engineering design and liquid transfer, the choice of pump is very important. Axial flow pumps and centrifugal pumps, as two main types, each exhibit unique advantages in different scenarios. If you need to find a reliable pump manufacturer, please feel free to contact LIANCHENG, we have more than thirty years of experience and a professional team.
.png)

